We are a well known worldwide supply and export Alloy steel plate in following countries:,Italy, Philippines, France,Ireland, Portugal, Gambia, Thailand, Ukraine, United Kingdom, Netherlands, South Africa, Spain, Turkey, Libya, Romania, Puerto Rico, Azerbaijan, United Arab Emirates, Pakistan, Ghana, Slovakia, Germany, Saudi Arabia, Afghanistan, Bolivia, Switzerland, Bangladesh, Taiwan, Oman, Egypt, Greece, Norway, Singapore, Bulgaria, Estonia, Belgium, Yemen, Hong Kong, Ecuador, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Belarus, Finland, Gabon, Iran, Canada, Argentina, Lebanon.
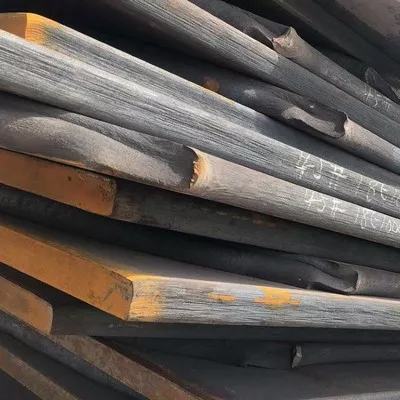
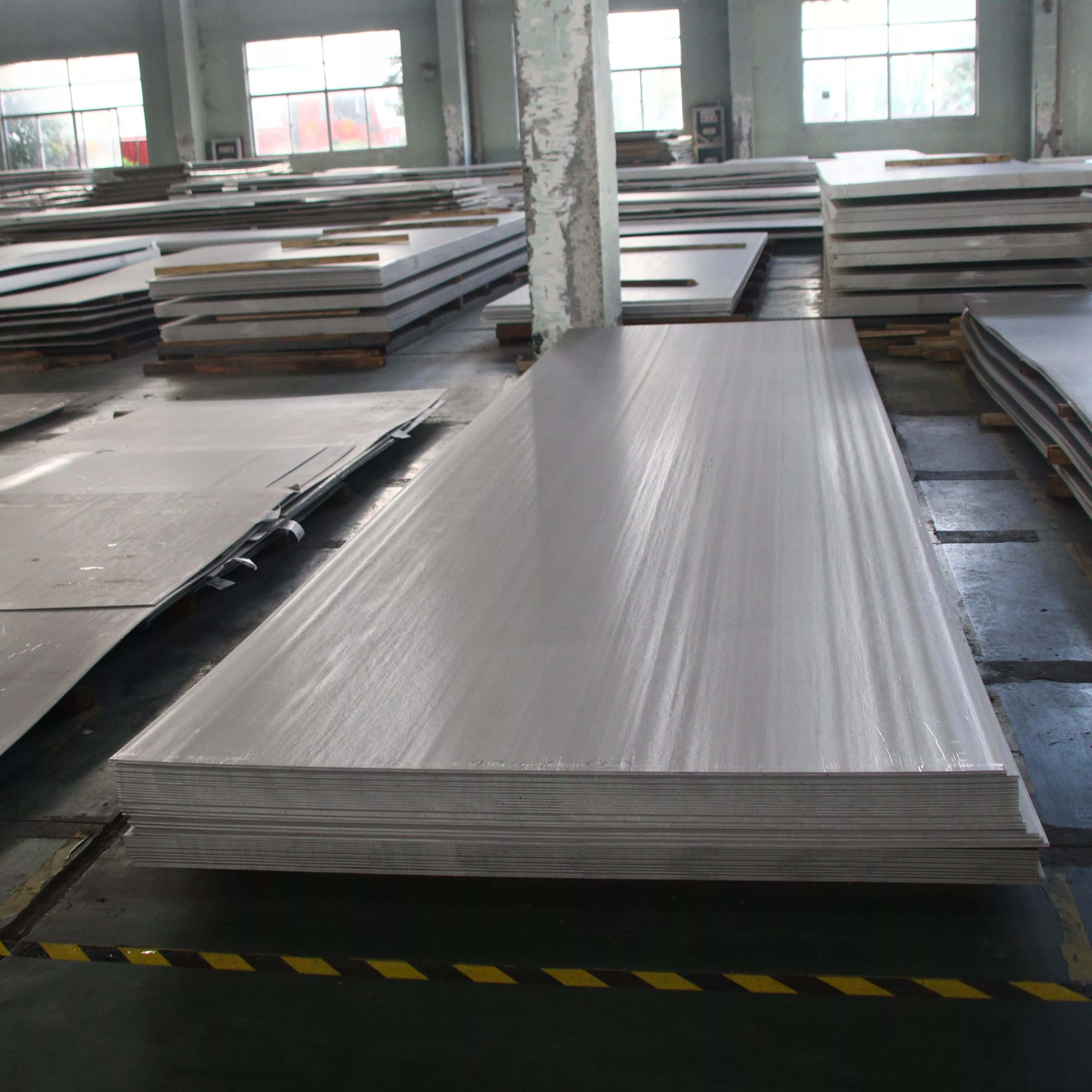
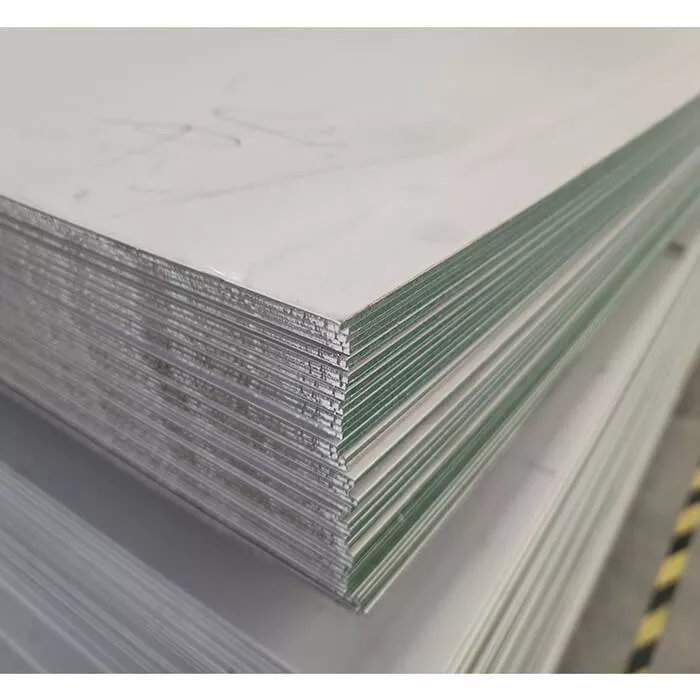
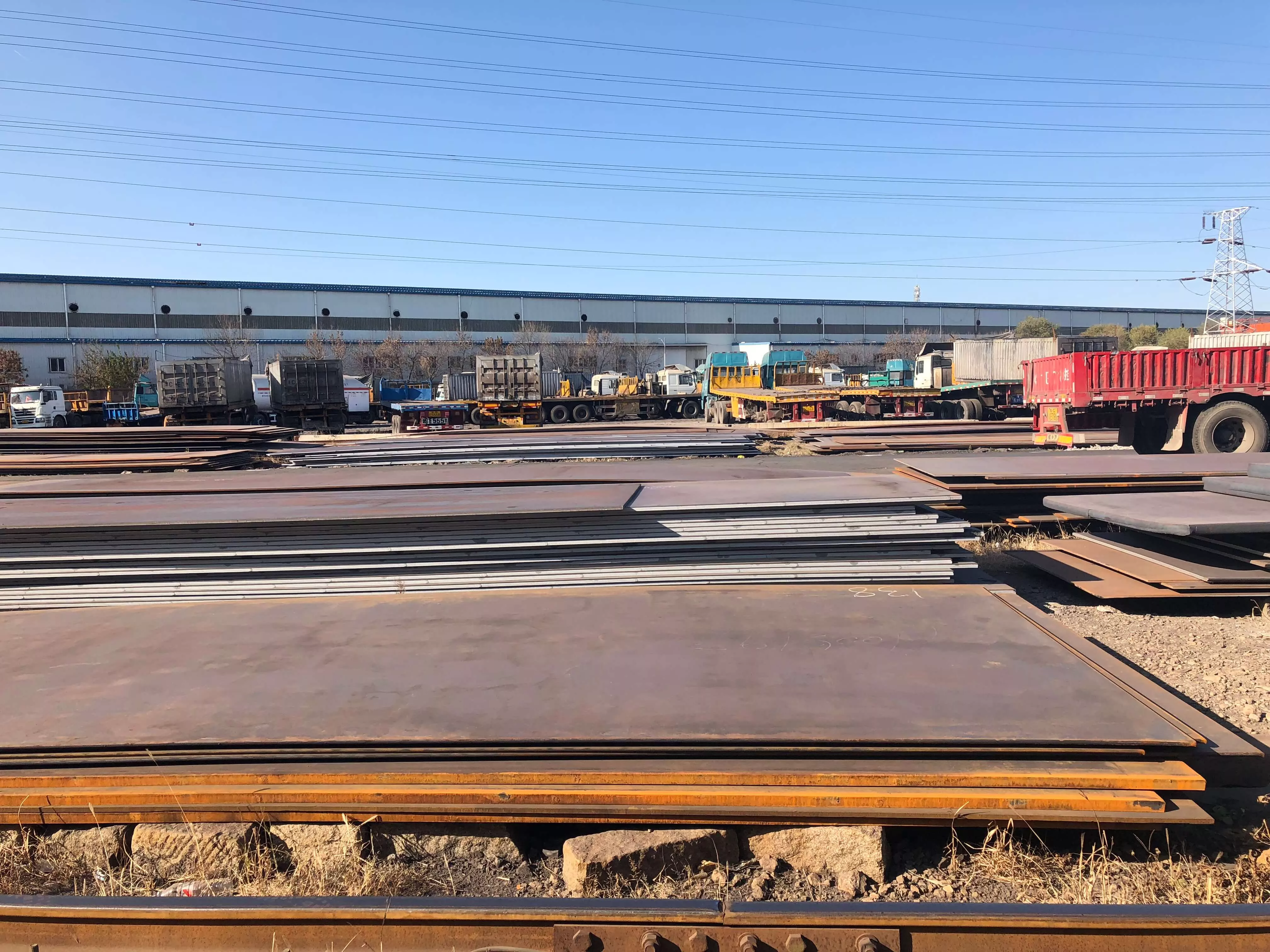
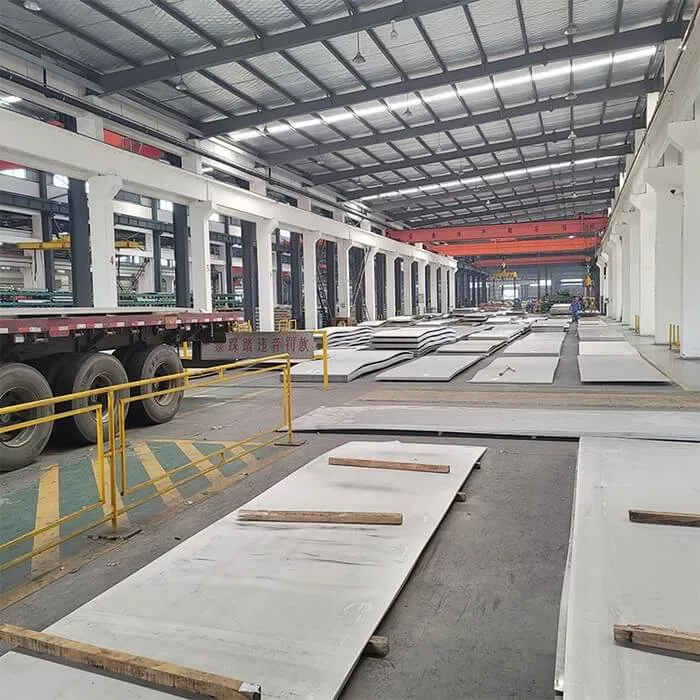
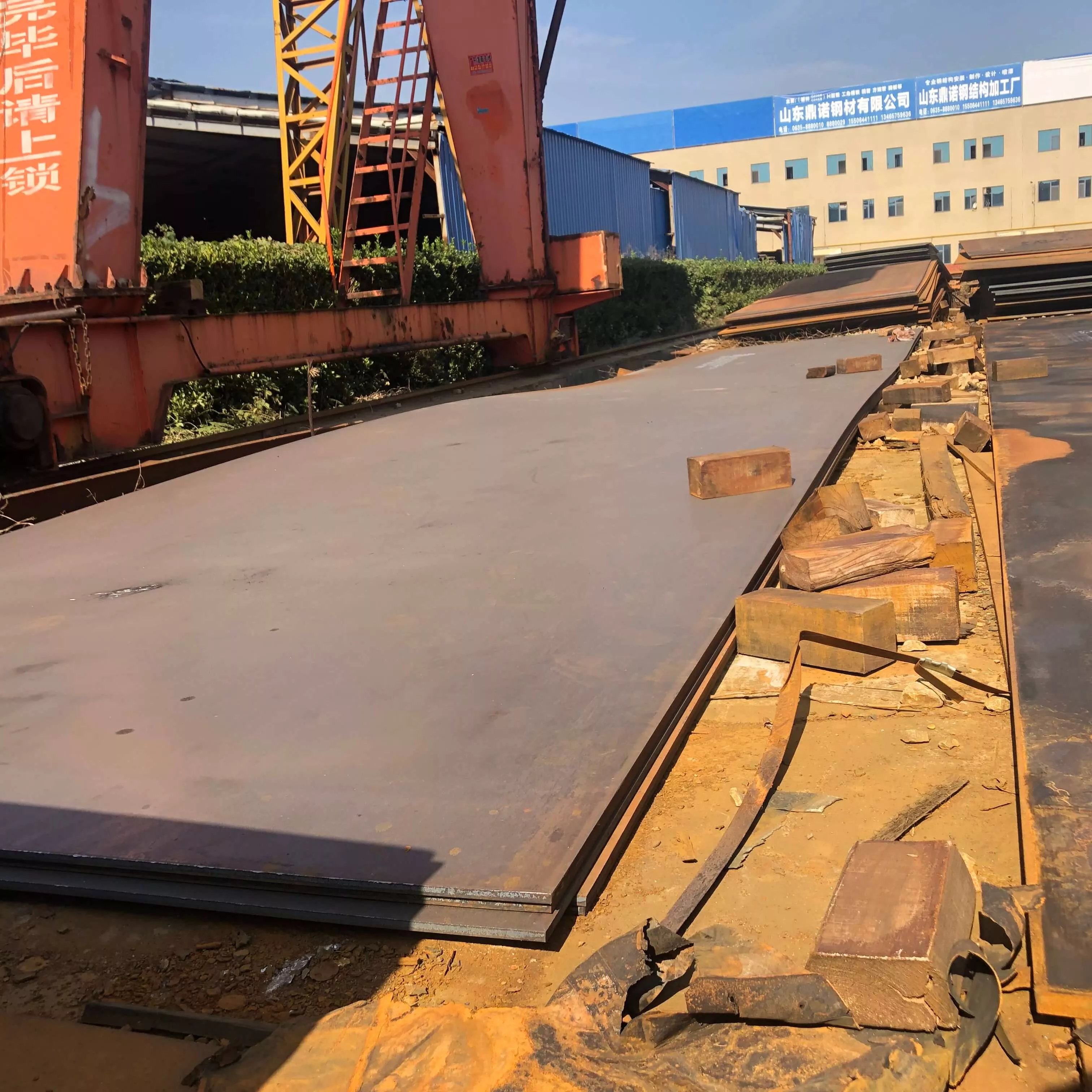
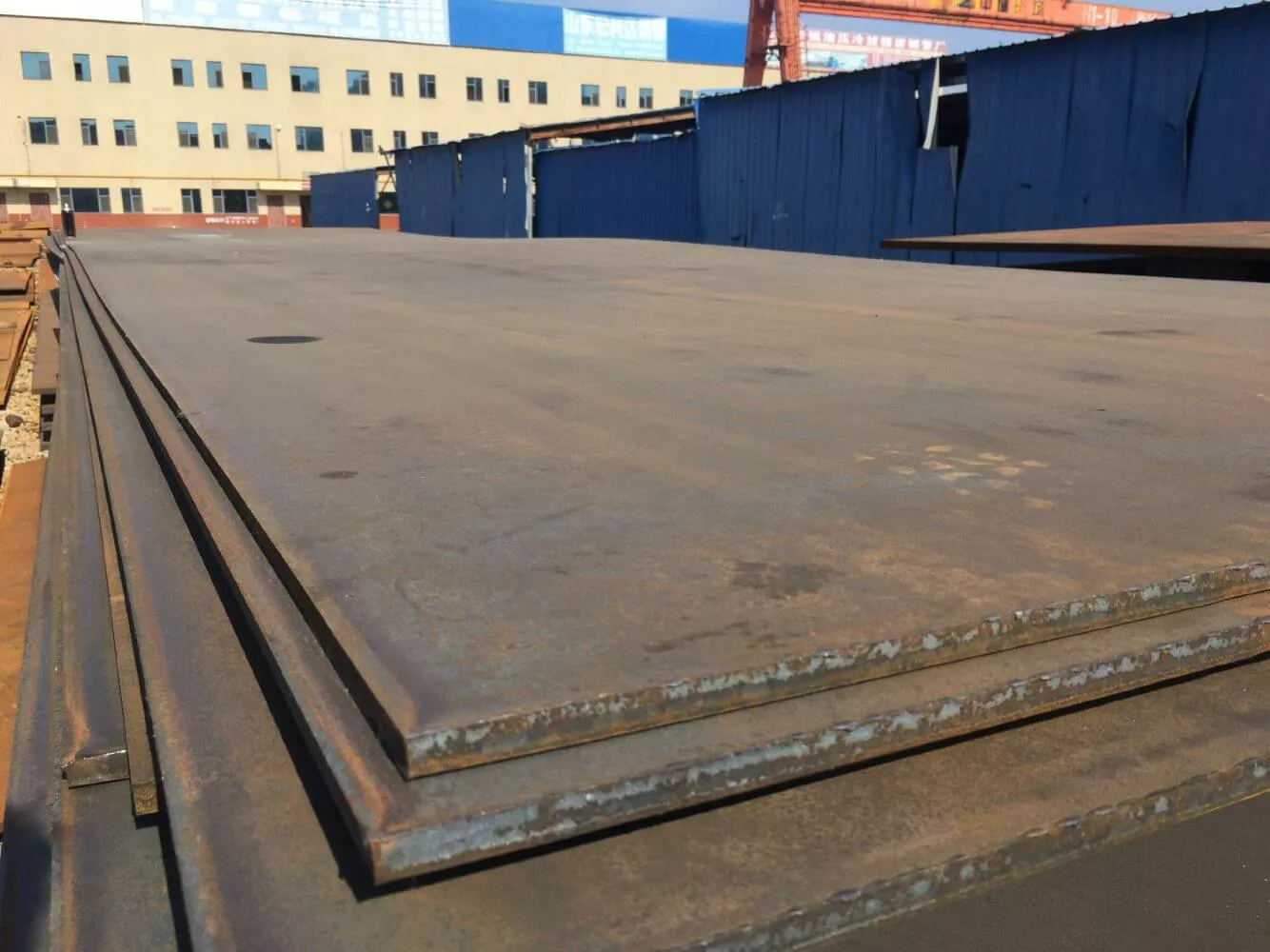
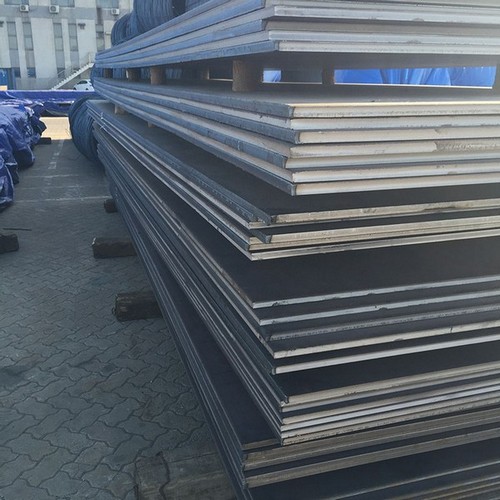
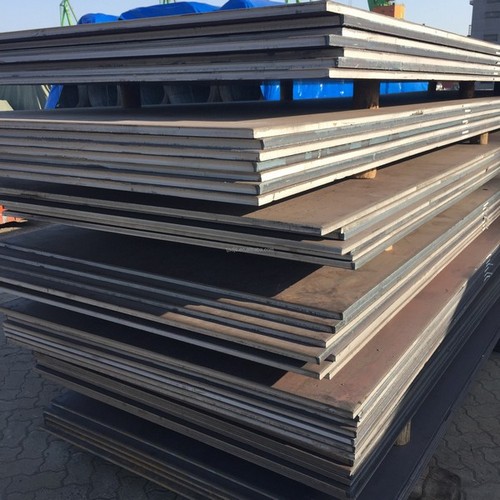
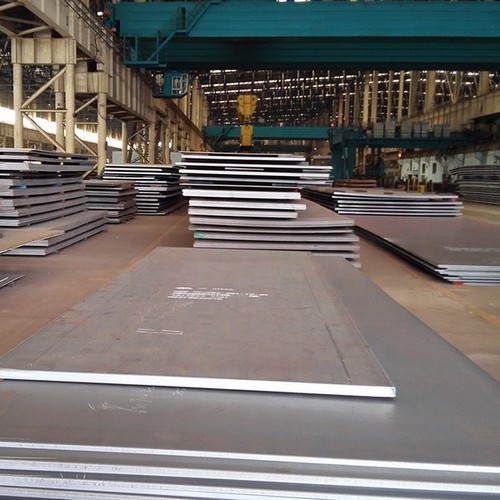













































 Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas

 Machine Manufacturing
Machine Manufacturing

 Marine Engineering
Marine Engineering

 Construction Industry
Construction Industry

 Chemical Industry
Chemical Industry

 Power Generation
Power Generation
 Product Categories
Product Categories

